Introduction
In this project we present strategies for point clouds reconstruction based on the automated acquisition and processing of Thermal and Multispectral imagery. The benefits derived from this methodologies consist in the implementation of customized low-cost data collection techniques, merging multiple datasets into a thermal-multispectral point cloud.
Context
Existing cities demand solutions to improve energy efficiency while lowering the production of CO2 emission. Energy awareness is becoming increasingly important nowadays thanks to the improving accessibility to Data, valuable in informing the decision making process for urban planners, supporting strategic choices for the incrementation of sustainable policies aiming at the reduction of environmental impact and footprint production. In the last 5 years, more than 50% of Barcelona pollution stations exceeded the mean average of PPM established by the European Union.
Methodology
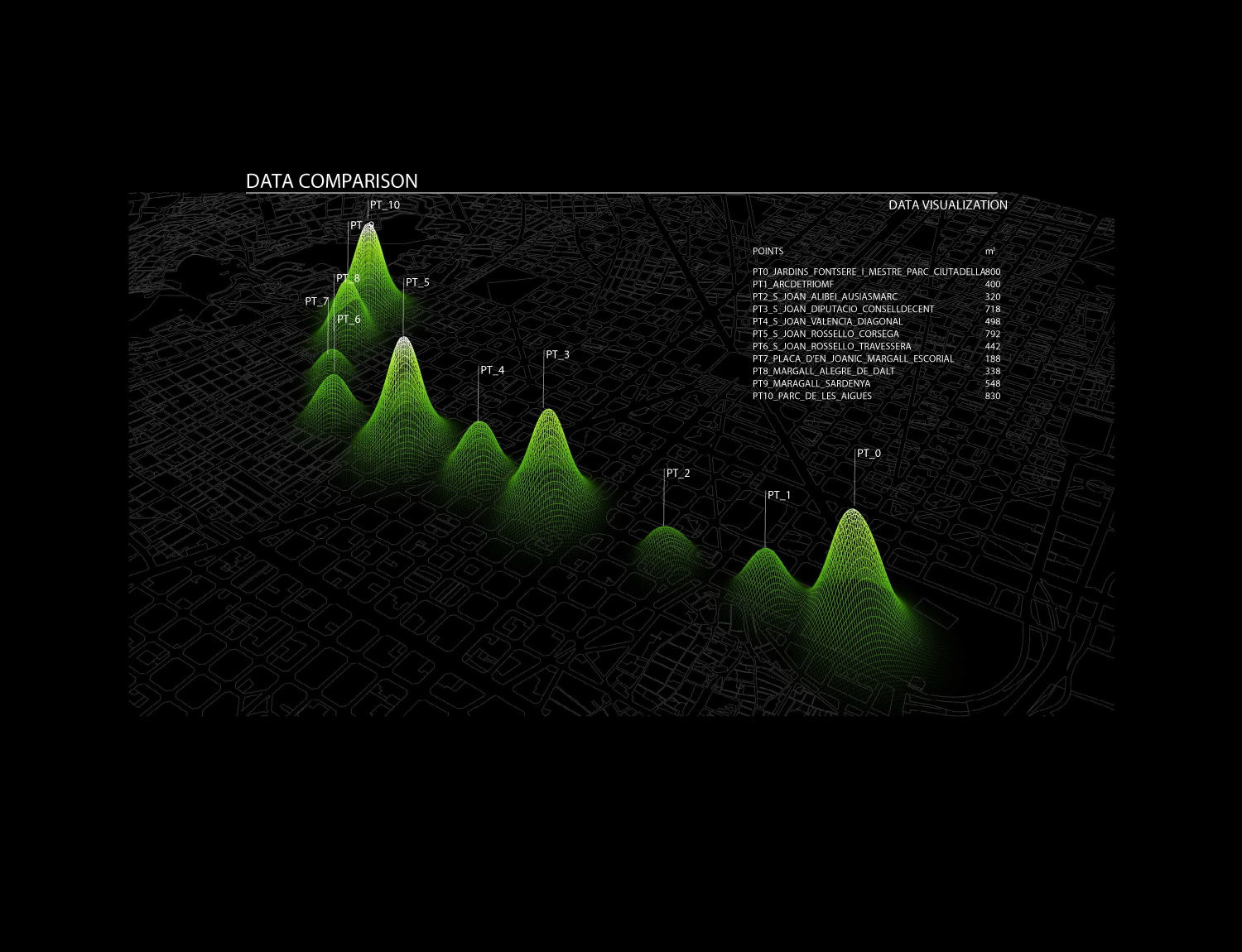
The operational context has been identified along 11 nodes of Paseo de San Juan in Barcelona. This choice is justified by the morphological and functional characteristics of this particular street, presenting strong differentiation of its section along its path, as presence of greenery, mobility and pedestrian paths structure.
Another relevant key aspect is the orientation of this street, mostly uniform, along the NW/SE axis. Those specific conditions have been considered valuable at the moment of comparing the different sections one with another.
Technology
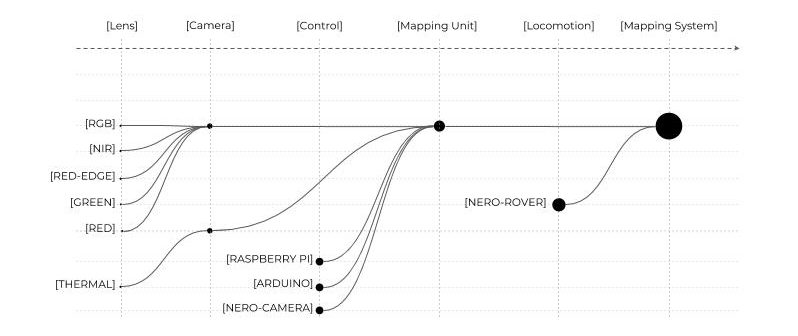
The proposed workflow is based on automated robotic collection of multispectral images through the implementation of a ground rover equipped with thermal and multispectral cameras.
This solution allow us to remotely gather images, programming the most efficient path to maximize the amount of data collection and minimize timing of the overall operation, in comparison with other existing processes.
The characteristics of the rover allow the machine to move nimbly along the different road paving, without interrupting vehicular or pedestrian mobility.
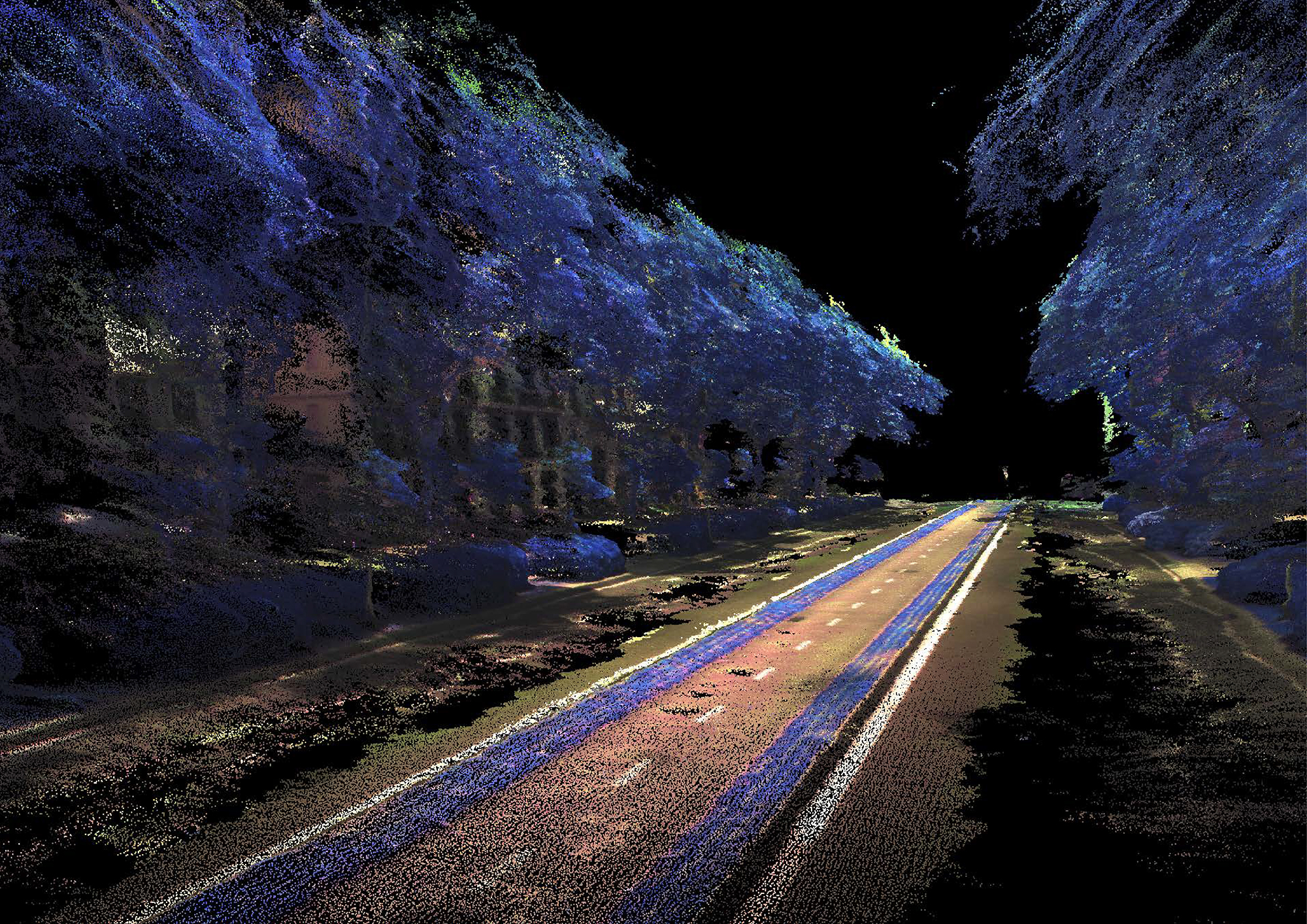
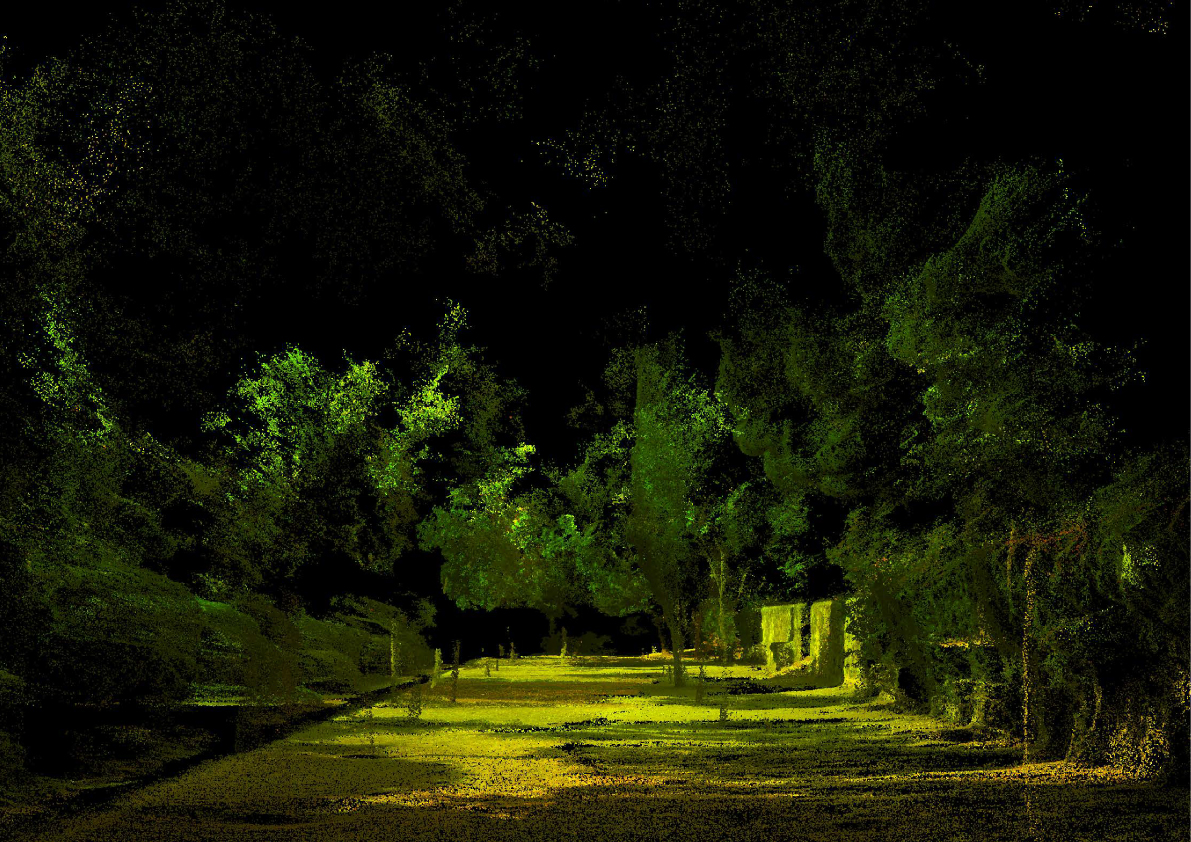
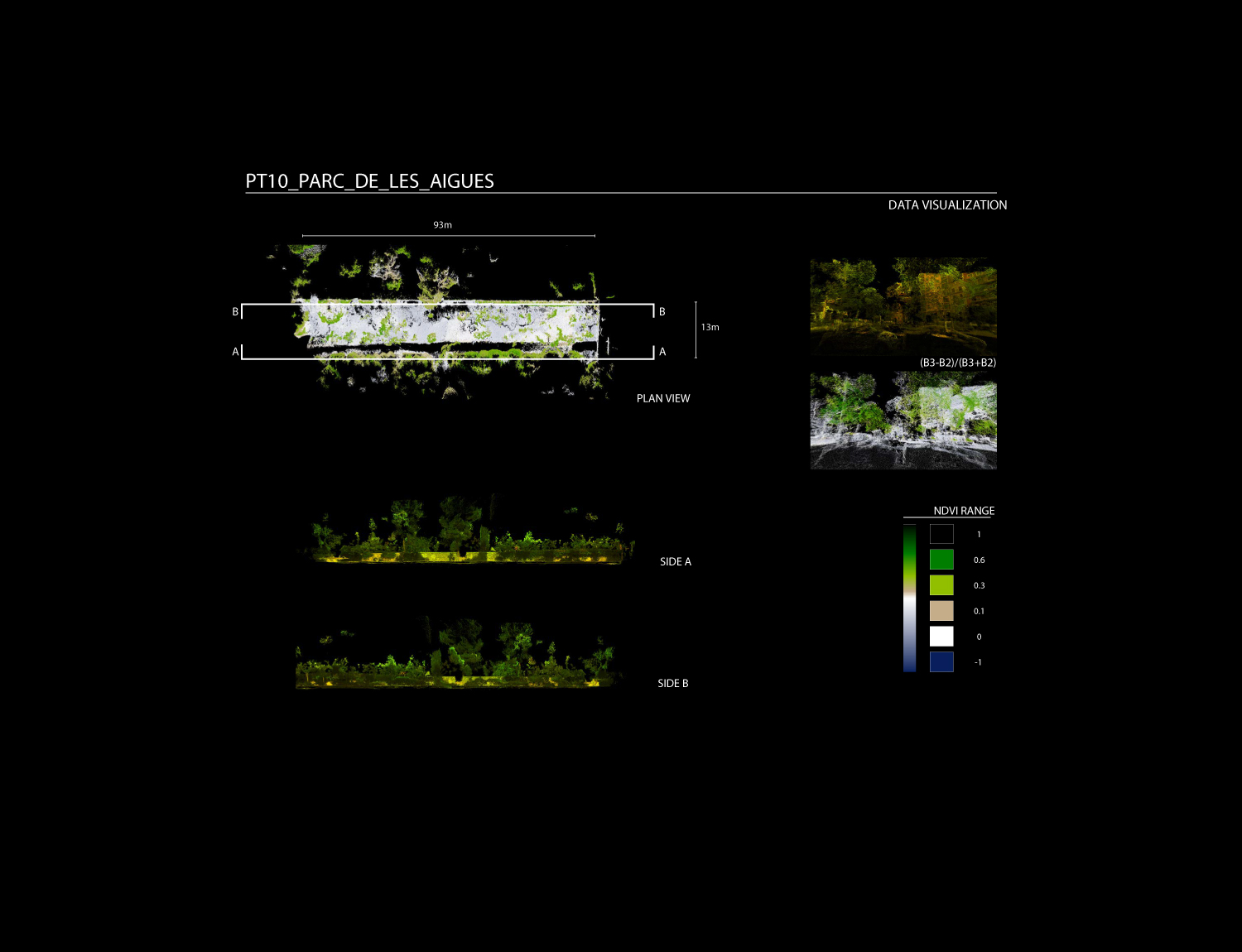
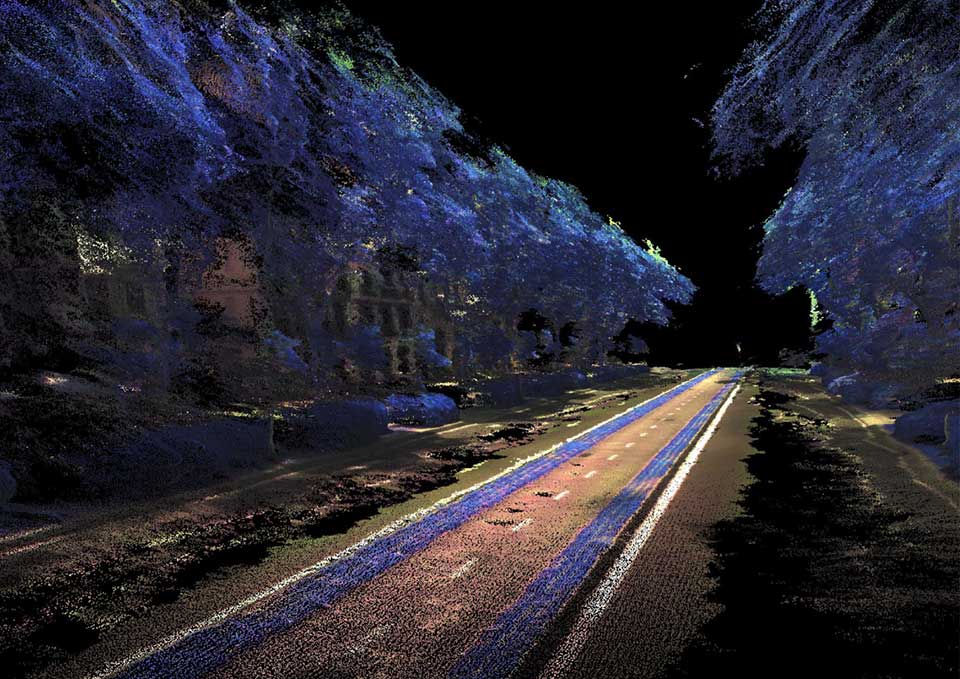
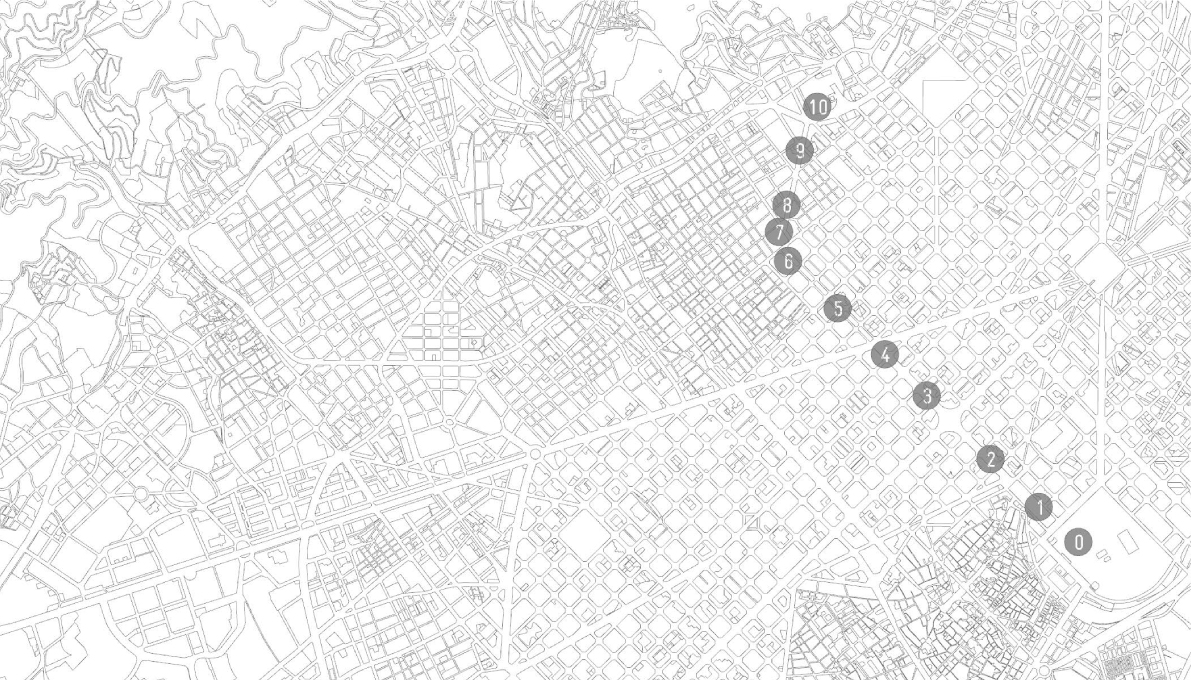
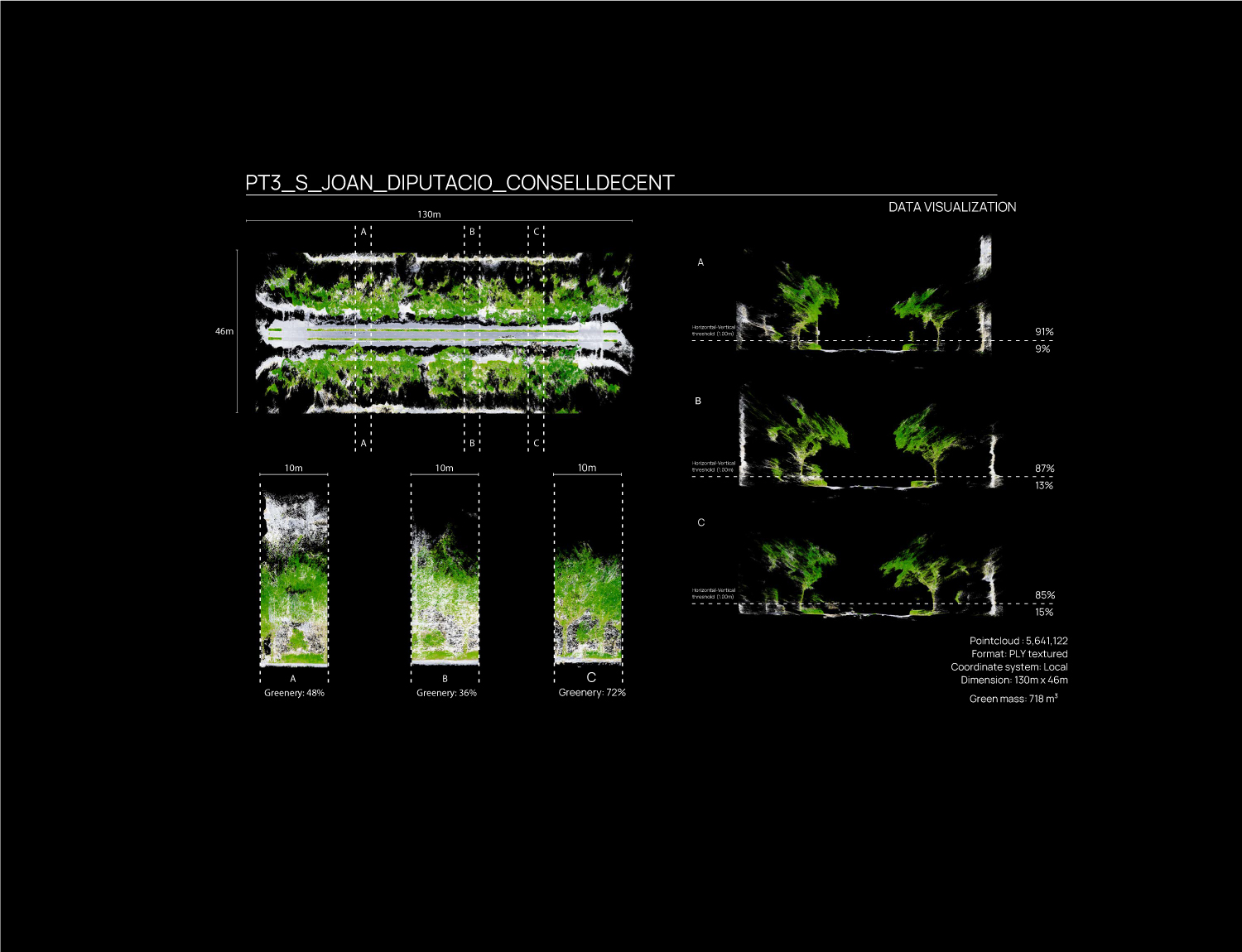
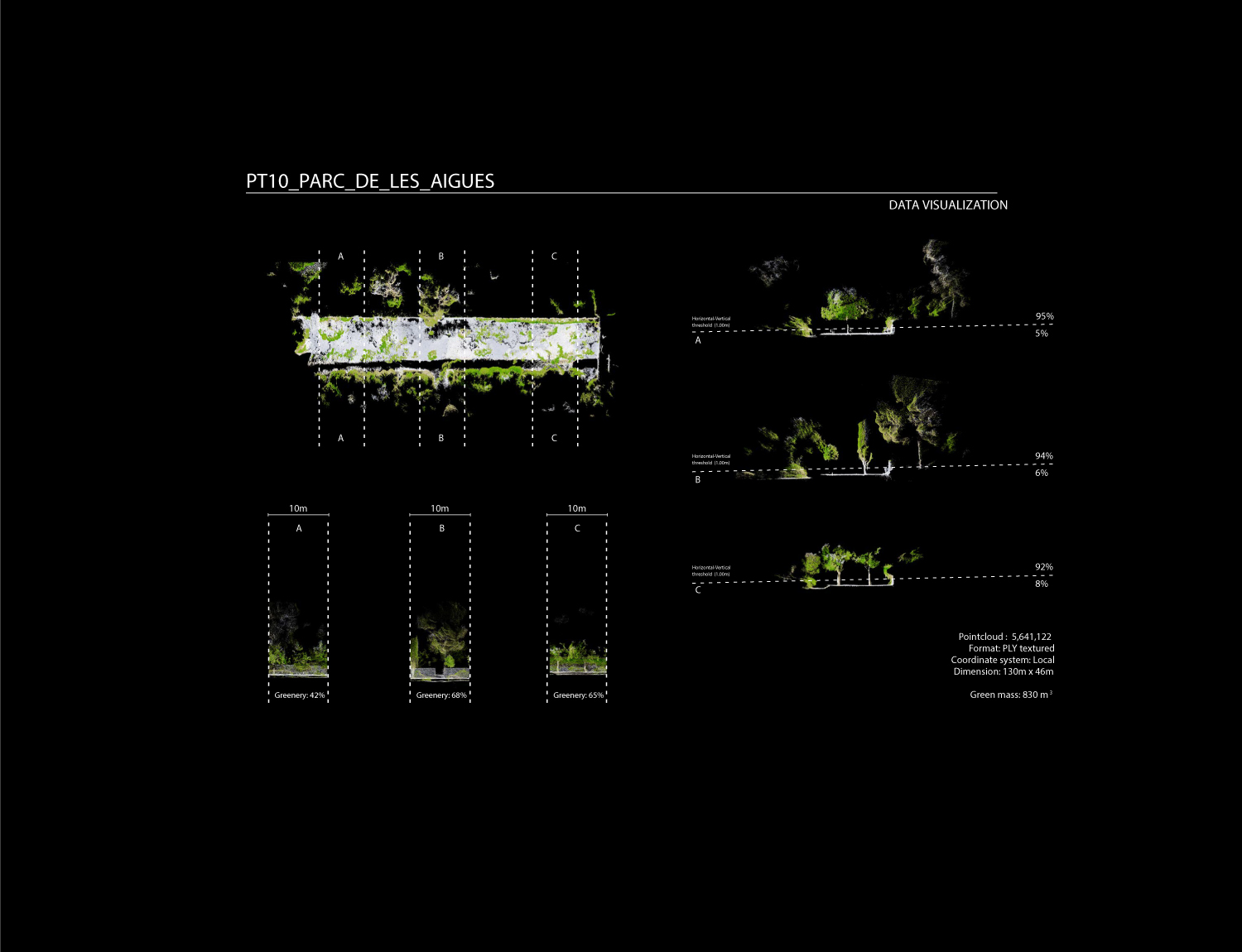
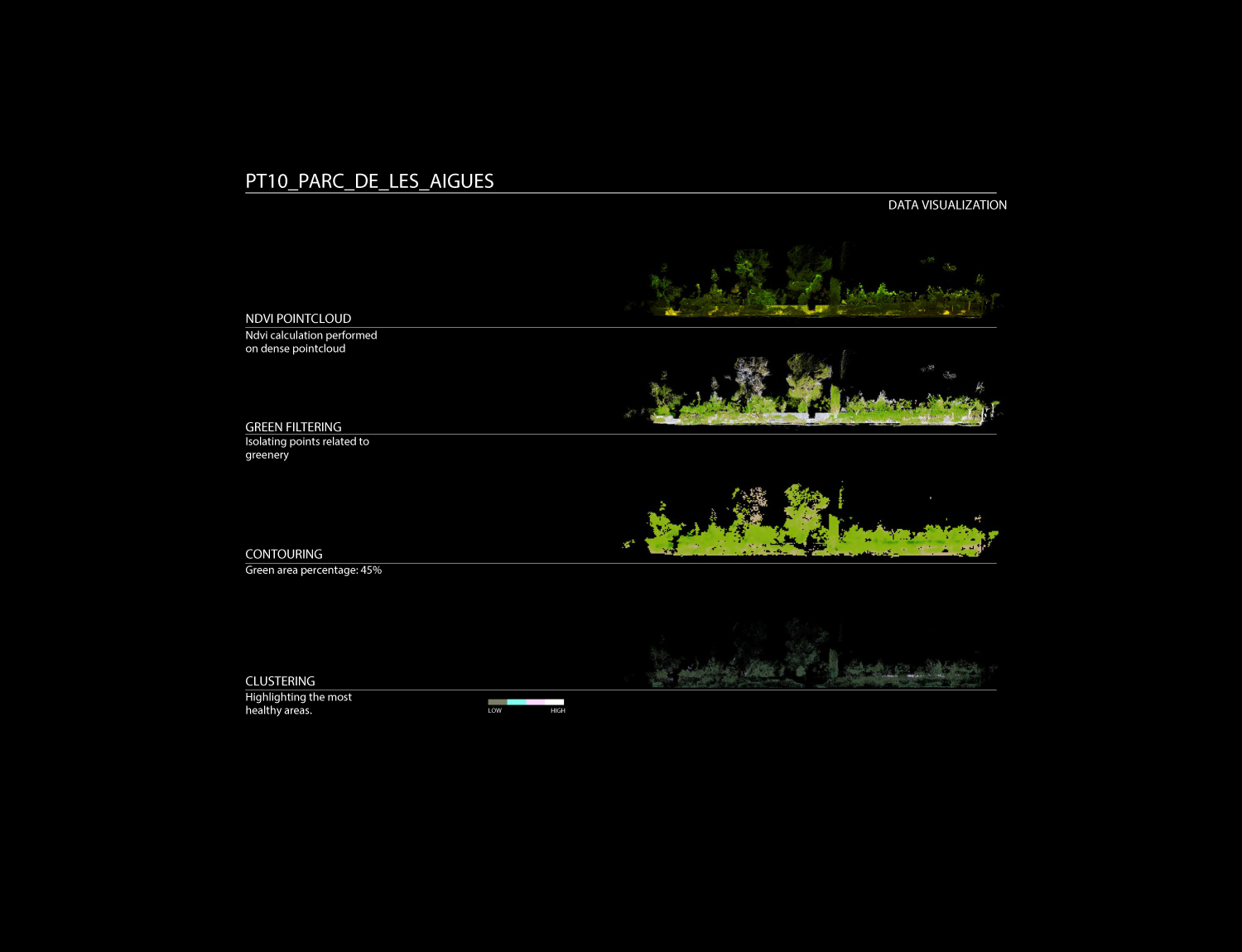
Data processing is developed through a specific customized method, generating one single point cloud, storing RGB, NDVI and Thermal Data over the same geometrical organization.
This method reconstruct and merge imagery into geometrically structured data, reconstructing the physical street environment, allowing to visualize thermal and NDVI values from the built and green envelope. As a final stage, the extracted 3D geometric model is saved as an industry standard file format for data interoperability.
Mapping Green Corridor
Highlight of the 11 selected points mapped along Paseo de San Joan in Barcelona.
Case study
P5 – PASSEIG SAN JOAN: Rossello-Corsega
This area is a portion of the Passeig de San Joan, located in between Carrer Rossello and Carrer Corsega. The area is characterized by a very small terrain inclination (2-3%). The buildings surround the two sides of the area and the relatives facades are for the majority covered by the greenery. The mapping strategy sees the robot moving along the area following the outer perimeter facing the camera towards the inner part of the area. A second turn is done moving the robot in the central part of the area while the cameras look towards the outer part of the area. This double path allow to minimize the blind spot of the camera and to obtain a much more reliable quality of the data.
Credits
Year → 2018 / Location Barcelona, Spain / Partnership Barcelona Regional
Contacts
HEADQUARTER
C/ de Cristóbal de Moura, 203,
08019 Barcelona, Spain
CONTACTS
P (+34) 937 420 927
E info@noumena.io